This week’s Amazon public relations push will no doubt go down as one of the odder public-facing strategies in tech. As some of the company’s biggest rivals were getting ready to virtually testify on Capitol Hill, the retail giant’s CEO of worldwide consumer business appeared to suggest that Amazon is not only as progressive as self-declared democratic socialist Bernie Sanders, but also more effective in achieving those leftist policies.
Ahead of the Vermont senator’s visit to Amazon’s Bessemer, Alabama fulfillment center, Dave Clark tweeted, “I welcome [Sanders] to Birmingham and appreciate his push for a progressive workplace. I often say we are the Bernie Sanders of employers, but that’s not quite right because we actually deliver a progressive workplace.”
The statement was unsurprisingly greeted with pushback from labor groups. The Retail, Wholesale and Department Store Union (RWDSU) sent TechCrunch a lengthy response from president Stuart Appelbaum to the odd statement:
How arrogant and tone deaf can Amazon be? Do they really believe that the wage they pay – which is below what workers in nearby unionized warehouses receive and below Alabama’s median wage – gives them the right to mistreat and dehumanize their employees, put their workers’ health and safety in jeopardy, require them to maintain an unbearable pace, which even Amazon itself admits that a quarter of their workforce won’t be able to meet, and to deny working men and women the dignity and respect they deserve.
The organization, which is helping facilitate the Bessemer warehouse’s union voting, goes on to cite high turnover rates and pay cuts amid the pandemic and founder Jeff Bezos’s ballooning wealth. The founder — who is set to step down as CEO some time in Q3 — reportedly added more than $72 billion to his net worth in 2020, as Amazon employees became essential workers amid COVID-19-fueled shutdowns.
For many in the U.S., Amazon’s online delivery service provided a lifeline, as many stores were forced to close over pandemic precautions. The Bessemer facility opened on March 29, just as the first wave was cresting in the U.S. The company was anticipating a potential strain on its resources as record numbers of Americans were suddenly forced to stay home and were otherwise avoiding in-person shopping at all costs.
“Our team at Amazon is thankful for the support we have received from state and community leaders, and we are excited to be a part of the Bessemer community,” Director of Operations Travis Maynard said at the time. “We’re proud to create great jobs in Bessemer with industry-leading pay and benefits that start on day one, in a safe, innovative workplace.”
After several years of negative coverage over its warehouse working conditions, it’s not surprising that the company has become proactively reflexive when it comes to working conditions.
“When New York City became the epicenter [of COVID-19], that’s when the Bessemer facility opened up,” Christian Smalls, a former Amazon worker-turned-critic said at TechCrunch’s Justice event earlier this month. “So the union got a head start on talking to workers. So that’s a gem for anybody or any union that plans on trying to unionize the building — that you have a facility in your community that’s about to open up, when opening, that’s the best time to connect with workers. That’s what happened last year. And as a result, the workers had seen what happened to the workers that were unprotected and they don’t want that. They want better for themselves.”
Next week, the RWDSU will begin tallying votes for what has shaped up to be the largest union push since Amazon’s 1995 founding, much to the company’s chagrin. In recent months, the company has been hoping to throw a wrench in the works. In January, it unsuccessfully appealed a ruling by the National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) that allowed workers to vote by mail, as more than 350,000 COVID-19 cases had been reported in the state since the beginning of the pandemic.
Amazon expressed concerns that mail-in voting would monopolize too much time and resources. “Union avoidance” firm Jackson Lewis suggested that such rules put employers at a disadvantage, “because eligible voters are given several days after receiving their ballots to return them to the NLRB, the impact and momentum of the employer’s voter education campaign is decreased. This does not exist in connection with a manual ballot election, where the employer may educate employees one-on-one until the last moment before they vote.”
The following month, Amazon ran anti-union ads on its streaming subsidiary, Twitch. The spots featured employees discussing why they were planning to vote no, and compelled people to visit Do it Without Dues, which blasted potential union membership fees.
“Amazon feels that it has to go to extremes like this in order to gaslight its workers about the dreadful working conditions at its Bessemer warehouse,” Appelbaum told the press in response to the ads. Twitch pulled the spots, adding that they, “should never have been allowed to run on [the] service.”
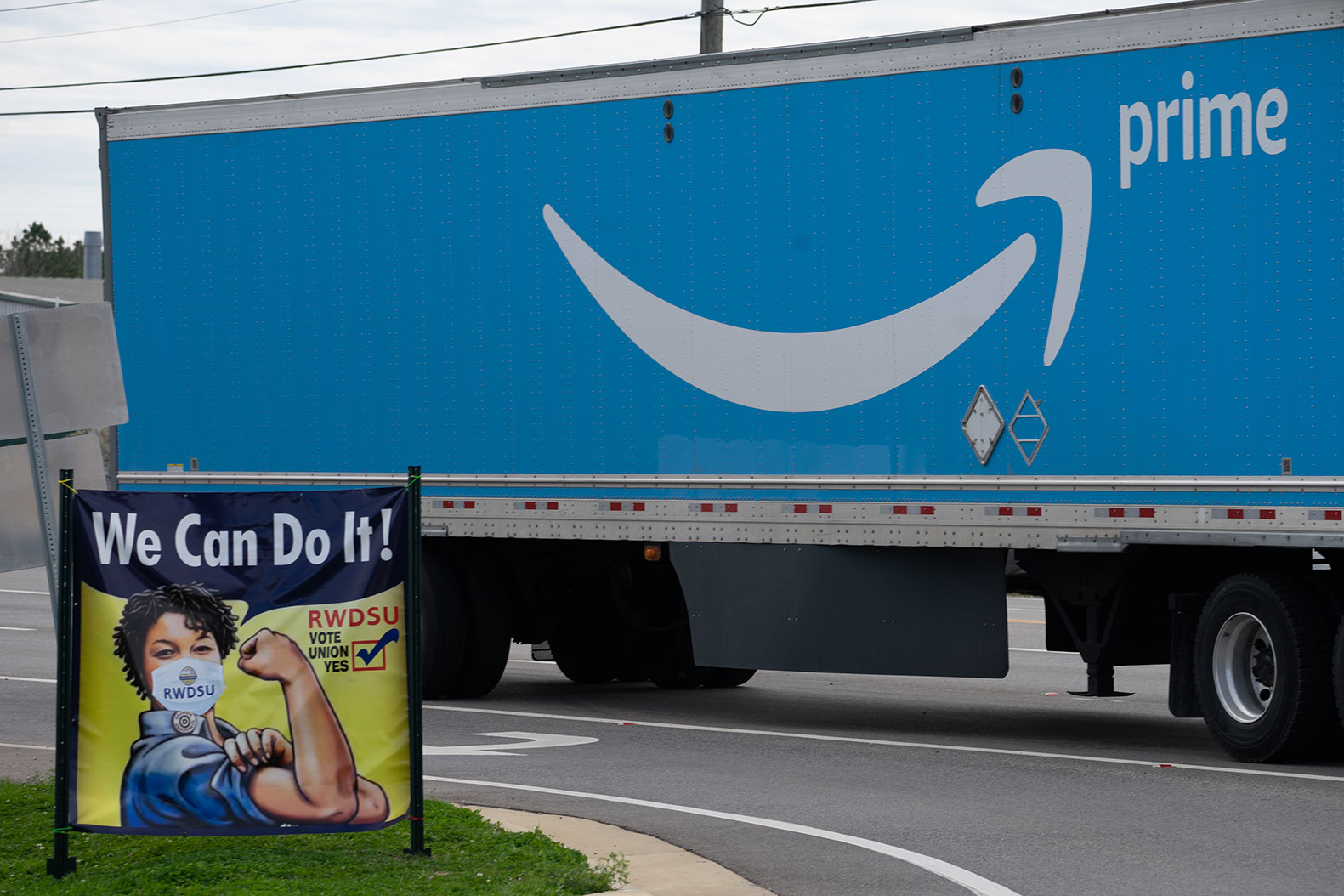

BIRMINGHAM, AL – MARCH 05: A truck passes as Congressional delegates visit the Amazon Fulfillment Center after meeting with workers and organizers involved in the Amazon BHM1 facility unionization effort, represented by the Retail, Wholesale, and Department Store Union on March 5, 2021 in Birmingham, Alabama. Workers at Amazon facility currently make $15 an hour, however they feel that their requests for less strict work mandates are not being heard by management. (Photo by Megan Varner/Getty Images)
Workers have continued to be critical of conditions in Amazon’s warehouses, frequently comparing the work to that of robots that have increasingly become their colleagues. Last week, New York Magazine published a piece from a Bessemer picker who describes long and tiring days on the floor.
“It really is not fair for employees to get fired for going to the bathroom,” the worker, Darryl Richardson, tells the magazine. “Sometimes the water in the bathrooms isn’t working on the floor, and you have to go down another flight of stairs to go to the bathroom.”
A number of similar stories have been recounted to the media over the years. Images of workers peeing in water bottles so as to not be docked pay — or worse — for taking a bathroom break have almost certainly become the most visceral.
When Wisconsin Rep. Mark Pocan called out Clark’s Sanders comparisons on Twitter earlier this week, an official account shot back, “We hope you can enact policies that get other employers to offer what we already do.”
Sanders has been a long-time critic of the company. The Vermont senator was one of a handful of progressive politicians who compelled Amazon to raise its minimum wage to $15 an hour, while criticizing massive tax breaks. In 2018, he introduced the Stop Bad Employers by Zeroing Out Subsidies (BEZOS) bill.
“The taxpayers in this country should not be subsidizing a guy who’s worth $150 billion, whose wealth is increasing by $260 million every single day,” Sanders told TechCrunch at the time. “That is insane. He has enough money to pay his workers a living wage. He does not need corporate welfare. And our goal is to see that Bezos pays his workers a living wage.” That November, the company relented, increasing minimum wage to $15 an hour — something that has since become a major talking point for Amazon.
Responding to Pocan’s comments about “union-bust[ing] & mak[ing] workers urinate in water bottles,” the Amazon News Twitter account wrote, “You don’t really believe the peeing in bottles thing, do you? If that were true, nobody would work for us. The truth is that we have over a million incredible employees around the world who are proud of what they do, and have great wages and health care from day one.”
Pocan’s reply was simple: “[Y]es, I do believe your workers. You don’t?”
In addition to past reports of warehouse workers and delivery drivers peeing in bottles, a new report from The Intercept notes that the act is “widespread,” due to workplace pressures. It cites an email from last May that also adds defecation into the mix.
“We’ve noticed an uptick recently of all kinds of unsanitary garbage being left inside bags: used masks, gloves, bottles of urine,” the email titled Amazon Confidential reads. “By scanning the QR code on the bag, we can easily identify the DA who was in possession of the bag last. These behaviors are unacceptable, and will result in Tier 1 Infractions going forward. Please communicate this message to your drivers. I know it may seem obvious, or like something you shouldn’t need to coach, but please be explicit when communicating the message that they CANNOT poop, or leave bottles of urine inside bags.”

Pro-union demonstration signs during a Retail, Wholesale and Department Store Union (RWDSU) held protest outside the Amazon.com Inc. BHM1 Fulfillment Center in Bessemer, Alabama, U.S., on Sunday, Feb. 7, 2021. The campaign in Bessemer to unionize Amazon workers has drawn national attention and is widely considered a once-in-a-generation opportunity to breach the defenses of the worlds largest online retailer, which has managed to keep unions out of its U.S. operations for a quarter-century. Photographer: Elijah Nouvelage/Bloomberg via Getty Images
As misguided or glib as the Amazon Twitter response may seem, it’s clear why the company has gone on the offensive here. “We’re not alone in our support for a higher federal minimum wage,” the accounted noted in the wake of the dustup with Pocan. The company adds that it has been pushing for a federal minimum wage increase following its own.
The push to unionize, meanwhile, has made strange political bedfellows, ranging from Stacey Abrams to Marco Rubio. Breaking with the customary party position, the Republican senator wrote in an op-ed, “Here’s my standard: When the conflict is between working Americans and a company whose leadership has decided to wage culture war against working-class values, the choice is easy — I support the workers. And that’s why I stand with those at Amazon’s Bessemer warehouse today.”
Rubio’s support of unionizing was tied, in part, to concerns over a “‘woke’ human resources fad,” but it’s still fairly uncommon for an event like this to find him on the side of the likes of Joe Biden, who had previously promised to be “the most pro-union president you’ve ever seen.”
Amazon will no doubt be keeping a close eye on Tuesday’s vote count, aware that the results will have a far wider ranging impact than the 6,000 workers currently employed at Bessemer. If unionization fails, the company will tout the results as vindication that its work force is perfectly happily without labor interference. A vote to unionize, on the other hand, could well embolden further unionization efforts across the company.