According to Startup Genome, Beijing, London, Silicon Valley, Stockholm, Tel Aviv are some of the world’s best startup ecosystems. The data and research organisation uses factors like performance, capital, market reach, connectedness, talent, and knowledge to produce its rankings.
Startup ecosystems from emerging markets excluding China and India didn’t make the organisations’ top 40 list last year. It is a known fact that these regions lag well behind in all six factors, and decades might pass before they catch up to the standards of the aforementioned ecosystems.
However, a Kenyan B2B management startup founded by Yacob Berhane and Wossen Ayele wants to close the gap on three of the six factors — access to capital, knowledge, and talent.
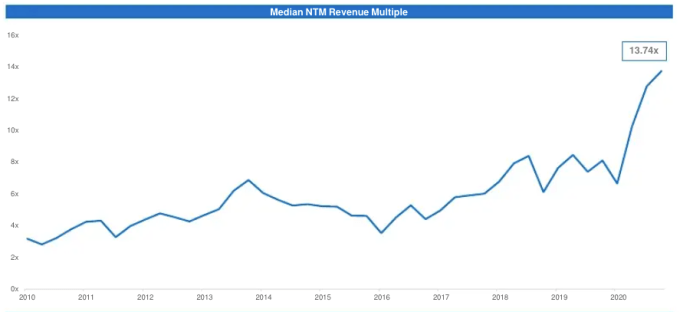
These issues, specifically that of access to capital, is heightened in Africa. For instance, only 25% of funding goes to early-stage startups in Sub-Saharan Africa compared to more than 50% in Latin America, MENA, and South Asia regions.
“We wanted to build a solution that will help startups be successful that otherwise would not have been able to get the resources they needed,” said CEO Berhane to TechCrunch. “This problem is especially acute in Africa because it’s particularly nascent, but this platform is designed for founders across emerging markets. So basically anywhere that doesn’t have a mature, healthy startup ecosystem.”
So, how is the team at Pariti setting out to solve these problems? Ayele tells me that in one sense, Pariti is like an unbundled accelerator.
In a typical accelerator, founders will need to go through an intense program where they are loaded with information on all the things a startup will likely need to know at some point in their growth. Whereas with Pariti, founders get the needed information or resources that are immediately relevant to helping them get to the next stage of the business.
A three-way marketplace
When a founder joins Pariti, they run their company through an assessment tool. There, they share pitch materials and information about their business. Pariti then assesses each company across more than 70 information points ranging from the team and market to product and economics.
After this is done, Pariti benchmarks each company against its peers. Companies in the same industry, product stage, revenue, fundraising are some of the comparisons made. The founder gets a detailed assessment with feedback on their pitch materials, the underlying metrics that they can use to develop their business and, their ability to raise capital down the line.
“This approach gives us an extremely granular view of their businesses, its strengths, weaknesses and allows us to triage the right resources to the founder based on their particular needs.”
It doesn’t end there. Pariti also connects the founders for one-on-one sessions with members of its global expert community. Their backgrounds, according to Ayele, run the gamut from finance and marketing to product and technology across a range of sectors. Pariti also provides vetted professionals for hire from its community if a founder needs more hands-on support building a product.
Ayele says founders can continue to go through this process multiple times, getting assessed, implementing feedback, and connecting with resources and talent.
On another end, Pariti allows investors to sign up on its platform, thereby collating data on their preferences. So once a startup wants to raise capital, the platform matches them with investors based on their profile and preferences.
“We’ve built an algorithm-based matching platform where we curate relevant deals to VC investors. We also simplify the investor reach-out process for founders, which is a huge pain point — especially in this ecosystem.”
Pariti’s investor platform
In a nutshell, Pariti helps founders connect with affordable talent, access capital and develop their businesses. Professionals can find interesting opportunities to mentor startups and get paid gig opportunities. They also get more exposure to the early stage ecosystem while tracking their progress, verifying their skills and increasing earning potential. Investors can run extremely lean operations with access to proprietary deal flow, automated deal filtering and on-demand experts to support due diligence, research and portfolio support.
According to the COO, the company has seen a tremendous amount of value built through the platform so far. A testament to this is an experience shared by Kiiru Muhoya, founder of Kenyan fintech startup Fingo Africa with TechCrunch, on how the platform helped him raise a $250,000 pre-seed round.
He said that after going through Pariti’s assessment ahead of a planned fundraiser, he realized that the market he was targeting was too small. Also, he needed to learn more about what VCs were looking for to be successful.
Muhoya decided to switch to being at the other end of things. Joining the expert platform on Pariti, he began to review companies and provided feedback to other founders. This led him to take some months off to pivot his business based on Pariti’s first feedback and what he had learned from the expert platform. He took his startup through another assessment on the platform and thus closed the round.
The company has made significant strides since launching in 2016. It has over 500 companies across 42 countries, 100 freelance experts, and 60 investors using its platform. Berhane also adds that five funds currently use Pariti’s operating system for their deal management.
“For us, I think we’re building the rails for how ventures are built and scaled in emerging markets. We have partners in place across emerging markets, including Latin America and India. We also have a strong interest in the United States, where we see a real need for our platform.” Berhane said.
It charges a subscription model for investors, but Berhane wouldn’t disclose the numbers. He says that Pariti will begin to charge a subscription fee for founders as well. Another revenue stream comes when investors or founders pay a certain transaction fee when using Pariti’s freelance experts for projects. The same happens when there’s any fundraise executed from the platform.
Talking about fundraising, the company recently secured an undisclosed pre-seed capital from angels and VCs like 500 Startups, Kepple Africa and Huddle VC.
But it hasn’t been smooth sailing for Pariti as one issue that has stood out in dealing with founders and investors is trust. Berhane says founders have shared some horror stories about engaging with investors, while investors have shared trust concerns about founders reporting false numbers.
Pariti tries to address this by providing NDAs for both parties where the company will not share founders data with investors until they want it to be. And investors won’t get deals that Pariti hasn’t thoroughly vetted.
Both founders of East African descent — Berhane from Eritrea and Ayele from Ethiopia — crossed paths a couple of times but took different routes to be where they are now.

Wossen Ayele (COO) and Yacob Berhane (CEO)
Ayele started his career at a consulting shop with offices across East Africa before moving back to the U.S. for law school. There, he got his first exposure to the early-stage startup world and worked with an emerging markets-focused VC fund.
“I could see how technology and innovation could play a role in helping communities – whether it’s through financial inclusion, access to essential goods and services, connecting people at the base of the pyramid to markets,” he said.
Upon graduation and completion of his legal training, Ayele headed back to Nairobi to get involved with its growing African startup ecosystem, where he and Berhane founded the company.
The CEO who studied finance and investment banking in the U.S. moved back to Africa to start a pan-African accelerator in Johannesburg, South Africa. While he has worked in managerial positions for companies like the African Leadership University and Ajua, Berhane spent most of his time brokering deals for them which ultimately led him to start Pariti.
“After helping businesses raise more than $20m and seeing how that money led to job creation and upward mobility for employees, I knew there was a path I could have that would be meaningful within finance. I continued to think about the growing asymmetry of access to capital, talent and knowledge in the startup ecosystem and the lack of infrastructure addressing it. Pariti was how we wanted to solve it.”