Tired of signing up for email newsletters? Then maybe it’s time to try out The New Paper‘s news digest, which arrives in the form of a daily text message rounding up the biggest headlines.
The Indianapolis-based startup is announcing that it’s leaving private beta testing. It raised $300,000 in pre-seed funding last year, including $80,000 from a pitch competition held by Elevate Ventures (the VC fund based by Indiana State).
Founders Michael Aft and John Necef told me that they started The New Paper with the intention of creating email newsletters at first (something Necef has experience with, having served as head of growth at The Hustle), but they decided that text messages offered the best way to, in Aft’s words, “do daily news right.”
“Think about the volume of email you get everyday,” he continued. “It’s this stressful, noisy, environment where you get spam and e-commerce messages. Text is easy, it’s clean, it’s extremely convenient, it’s intimate.”
In fact, Necef said that “a common anecdote” they’ve heard from early subscribers is the fact that they sign up for email newsletters “with the best of intentions” but then those newsletters end up sitting unread in their inboxes. (Think of it as the digital equivalent of those piles of unread New Yorkers.)
Of course, the fact that text messaging is such a personal channel also means that readers aren’t likely to stick around unless they’re actually getting what they want. But Aft said he embraces the challenge of meeting that higher bar: “You’re never going to forget that you subscribed.”
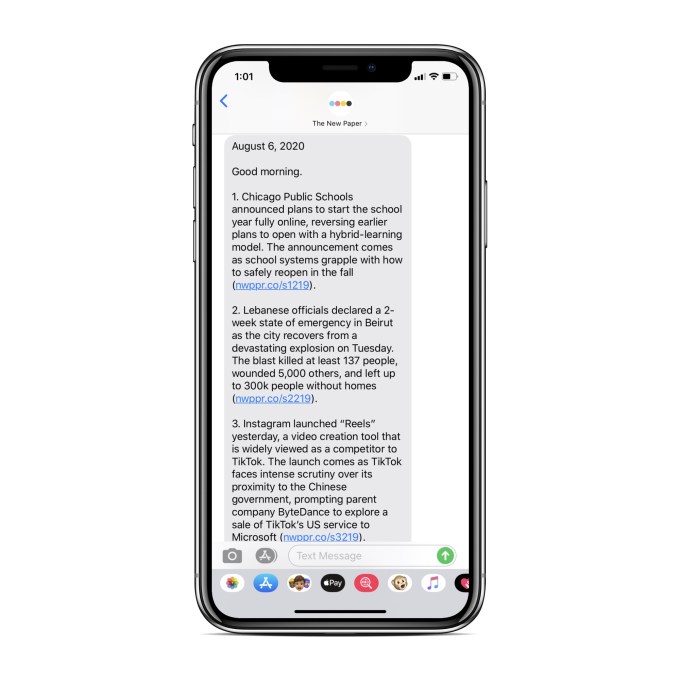
Image Credits: The New Paper
In fact, The New Paper needs to provide value not just because it’s delivered via text message, but because it’s a paid product — after a weeklong free trial, it costs $5 per month. And more than 7,000 paying subscribers have already signed up.
Currently, the digest consists of six headlines, all linking to reporting from other publications, plus a link to The Daily Dash, which provides a high-level snapshot of stock market performance, the current state of the coronavirus pandemic and more.
Both Aft and Necef emphasized that The New Paper’s approach is “fact first.” Of course, there are plenty of news organizations that tout their objectivity and devotion to accuracy, but the pair seemed particularly determined to present their readers with a “common set of facts” about a story that everyone can agree on, regardless of their political leanings.
To illustrate the company’s approach, Aft pointed to the recent report on Russian election interference by the Senate Intelligence Committee. Rather than trying to make any “second order conclusions” about the report — conclusions that could be influenced by a writer or editor’s political beliefs — he said The New Paper focused on what was factually indisputable, namely that the committee had released its report.
As soon as he said that, I imagined editors past and present tearing their hair out — not because they’re liberals determined to make the Trump Administration look bad, but because the report’s findings (that Russian intelligence worked to interfere with the election, and that members of the Trump campaign were happy to accept the help) is the real news, rather than the simple fact of the report’s release.
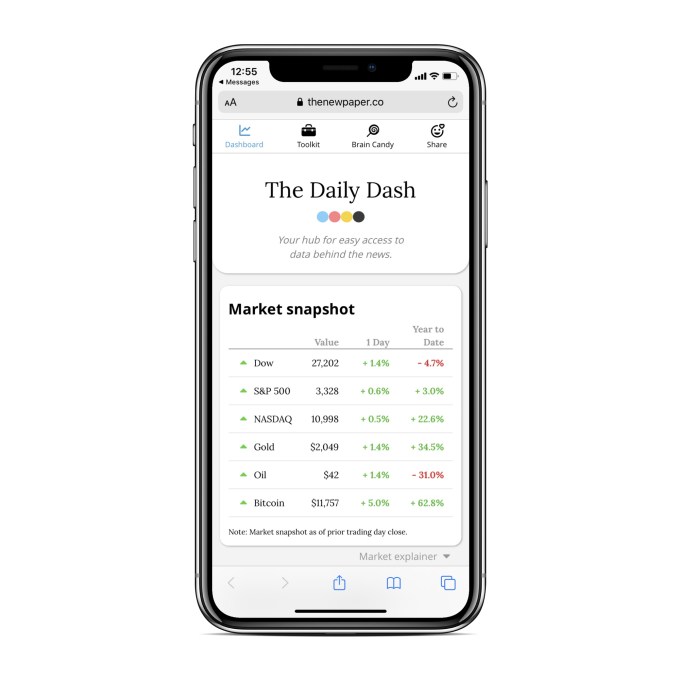
Image Credits: The New Paper
In other words, emphasizing objectivity and facts sounds good, but it also risks leaving out crucial context or analysis. Plus, it’s become increasingly clear that facts rarely change people’s minds.
Still, despite my quibbles with the approach, I’m happy to report that I’ve been receiving the digest for the past week, and I’ve found it to be a convenient, comprehensive catch-up on the day’s news, with links that make it easy to learn more.
For now, Aft and Necef are writing the digest themselves, though they said much of the ranking and sorting is done by algorithms. Over time, they’re hoping to hire on both the technology side and the editorial side. They also plan to expand into other channels like email and voice.
Asked whether the subscription business model means that they don’t have to pursue a mass audience, Aft replied, “We think it’s so critically important to give people a common set of information. To make this a viable business model, do we need to be 100 million strong? Of course not. Is that the goal we’re targeting? Absolutely, because we are so passionate about the problem.”